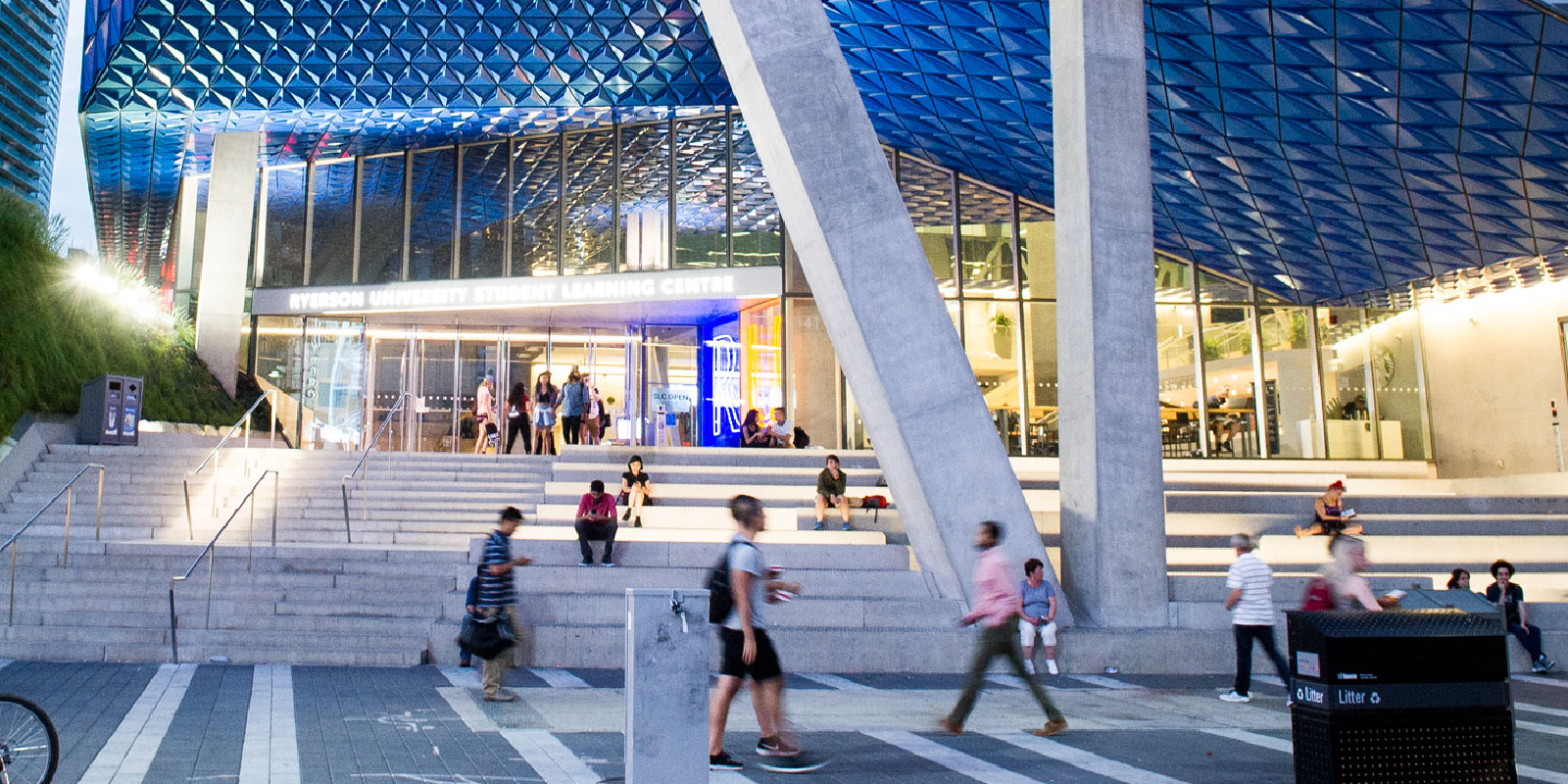
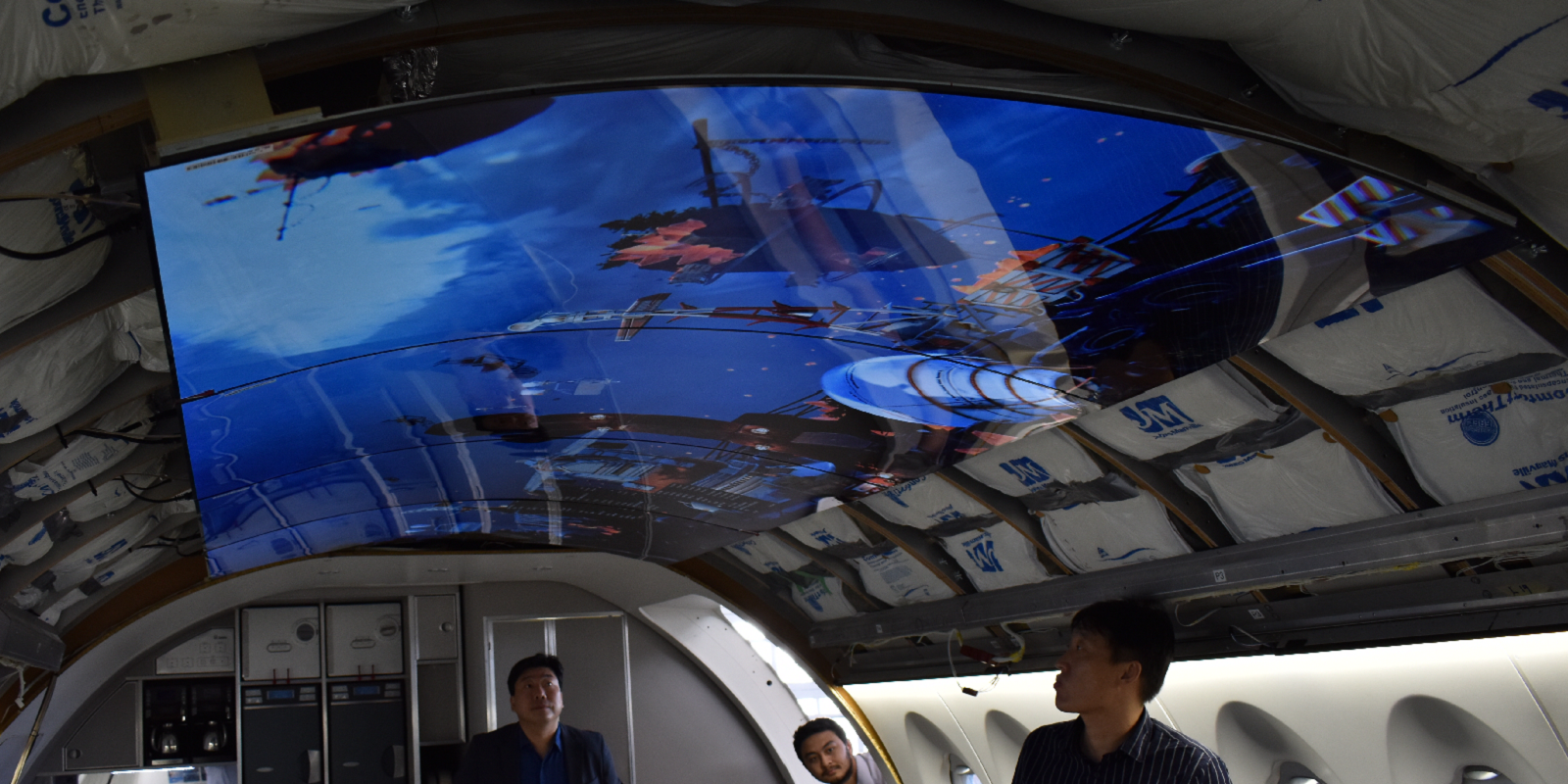
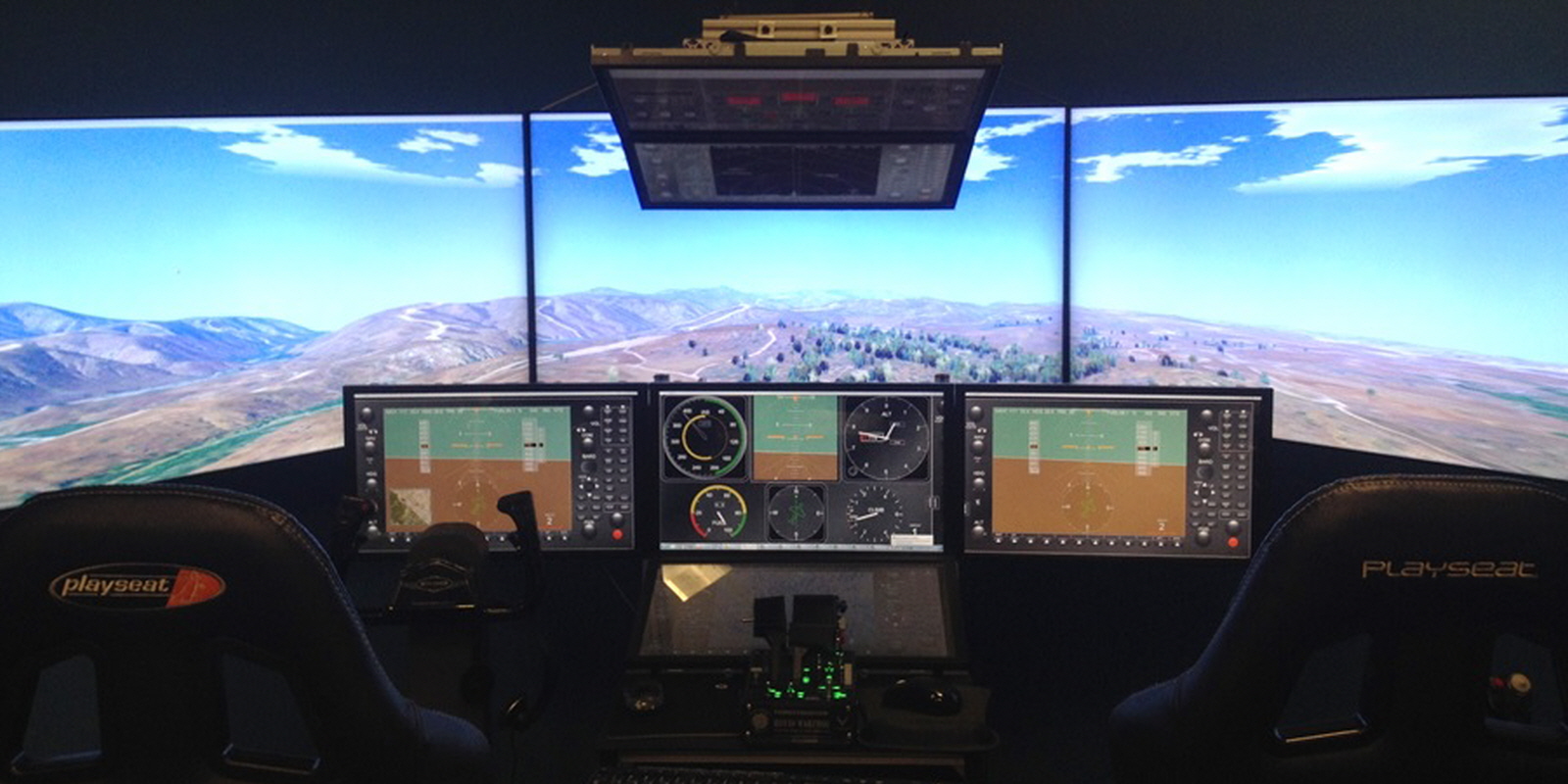
MIMS Lab has been exploring the potential usage of various Extended Reality (XR) technologies for aviation applications since 2013. It has been testing and developing headsets ranging from Oculus Rift DK2, Microsoft HoloLens 1, and HTC Vive to Varjo XR3, Oculus Quest 3, and Apple Vision Pro.
Virtual Reality (VR)
Apple Vision Pro
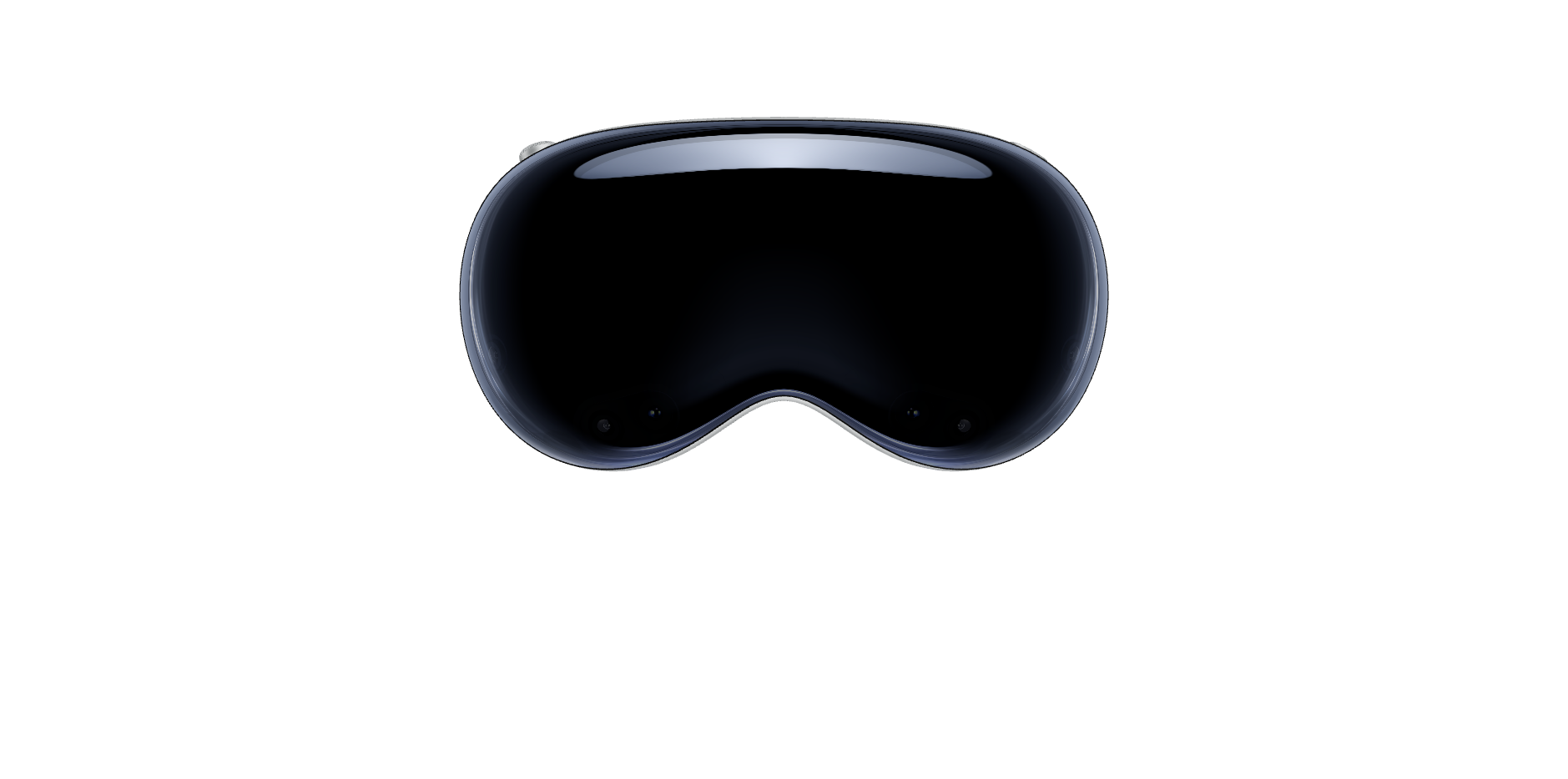

figure from Apple Vision Pro
Apple Vision Pro is one of the latest addition to our collection of XR devices. Released on June 2024, Apple Vision Pro is the first head-worn display designed by Apple, Inc., with an intention to provide highly intuitive XR experience using their camera passthrough resolution of 1920 x 1080, 4K (4096 x 2160) display resolution per eye, with a camera system specifically for depth sensing and facial tracking in real time. Similar to its AR predecessors between 2016 and 2023, it contains various input methods, including eye tracking, hand gestures (e.g. pinching, spreading, and tapping), voice commands (via Siri), and digital crown. With its capabilities, it can be very useful in projects related to 3D modeling and design, product prototyping and testing, data visualization, remote collaboration, training and education, and field service and maintenance.
Varjo XR-3
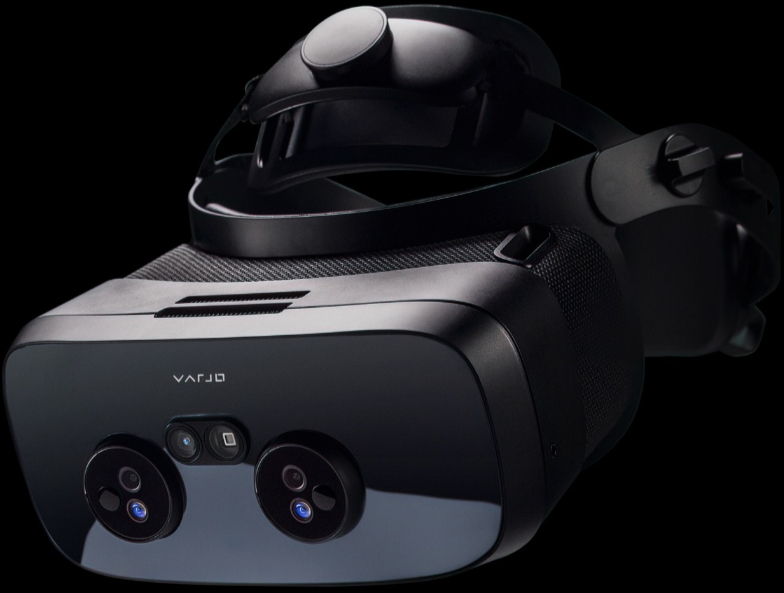

figure from Varjo XR-3
Varjo XR-3 is the most advanced XR headset currently owned by the MIMS Lab. Its capability to provide a camera passthrough visualization through its ultra-low latency, dual 12MP camera system at 90Hz, and a full bionic display with human-eye resolution makes blending real and virtual elements seamlessly a possibility. Its display features a focus area with a resolution of 1920 x 1920 pixels per eye using uOLED technology, and a peripheral area of 2880 x 2720 pixels per eye using LCD technology. Its primary forms of input include using Valve trackers and controllers, but it also supports camera-based hand tracking similar to that of the Meta Quest. This headset, by Varjo was recently approved for various VR flight simulation training by the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) and the European Union Aviation Safety (EASA).
Windows Mixed Reality HMD

figure from Windows Mixed Reality
Since its production, HoloLens 1.0 was criticized by many developers for four reasons: high cost, lack of immersion, limited Field of View (FOV) and heavy weight. To account for all these problems, Windows Mixed Reality Program was introduced. Within this program, computer technology companies such as Acer, HP, Dell, Samsung and Lenovo have been producing Mixed Reality headsets and accessories since early 2017. They are lightweight computer - operated HMDs each equipped with a pair of depth IR cameras for inside-out tracking, and high resolution graphics with an FOV between 85 - 110 degrees for high quality immersion. It can operate many HoloLens and other Universal Windows Platform (UWP) applications or allow the users to control their Windows 10 system in Virtual Environment (VE) using either one of the following input devices: keyboard and mouse of the PC, XBox Gamepad and Windows MR Motion Controllers.
HTC Vive
figure from VIVE US website
HTC Vive is a Mixed Reality system developed by HTC Corporation and Valve Corporation in the year 2015. An HTC Vive System is equipped with two IR base stations for outside-in tracking, handheld VR motion controllers with 24 sensors for precise haptic feedback, and an MR system headset with a front facing camera for MR experience and 32 sensors for precision tracking. The headset has a field of view of about 110 degrees for improved visual immersion.
Pimax 5K Plus
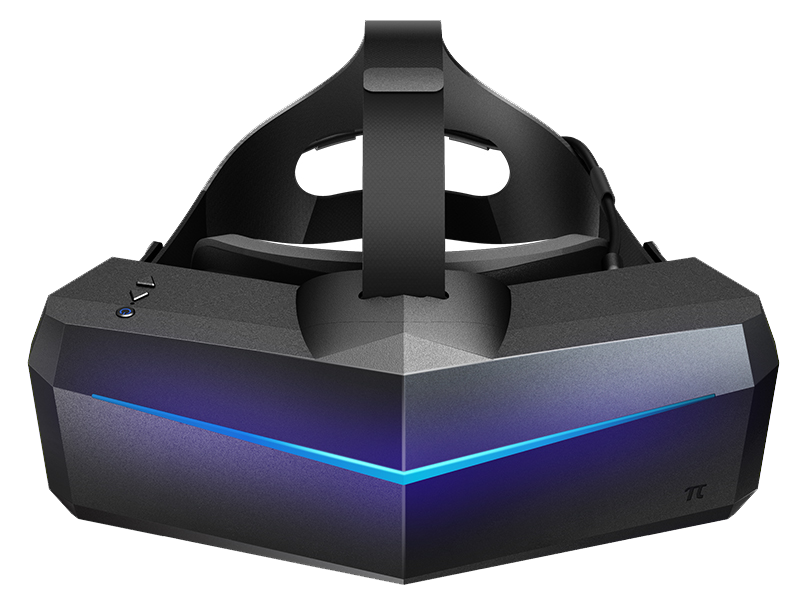

figure from Pimax website
Pimax 5K PLUS is another outside-in tracking based Virtual Reality system with an ultrawide 200 degrees field of view and 2.5K resolution per eye. It is compatible with the base stations and controllers of the HTC Vive system as well as Valve Index making it adaptable among a wide variety of VR developers. In addition, its wide FOV of 200 degrees, high refresh rate of 120 Hz, and high resolution of 5120 x 1440 makes it a highly immersive experience for flight simulation and various other applications, while reducing tunnel vision (also known as peripheral vision loss).
Oculus Quest Wireless Standalone Headset

figure from Oculus Website
Oculus Quest is an extremely powerful VR headset capable of running high quality 3D applications wirelessly and without relying on an external computer. Similar to WMR headsets, this headset operates based on the inside-out tracking mechanism, and therefore, does not require external sensors to track the environment, or use its 6-DOF lightweight Oculus Touch Controllers. In fact, it is the first VR headset to allow hand-tracking. In other words, its onboard camera sensors can detect the user's fingers and hands and use them as an input method on selective applications. Additionally, it is also one of the few headsets to employ AR outside of the room-scale to prevent potential accidents in the real environment.
Oculus Rift Goggles

figure from LabReporter Website
Oculus has a very small, high resolution screen on the inside of the headset. The image is then split into two viewable regions and magnified by two separate eye lenses. One major advantage of Virtual Reality goggles is that various hazards can be visually marked to make them stand out.
Augmetned Reality (AR)
Microsoft HoloLens 1.0

figure from Windows Dev Center website
HoloLens refers to a pair of Mixed Reality goggles that blends holograms into the user's Field of View (FOV) of the physical world. While VR immerses the user in a simulated world, the MR enables holograms to look and sound like they're part of the user's world by understanding the user's environment. HoloLens embraces Augmented Virtuality (AV) and Augmented Reality (AR) to create the Mixed Reality (MR). It includes multiple sensors, including a Mixed Reality capture, an ambient light sensor, an Inertial Measurement Unit (IMU), four environment understanding cameras, one depth camera, one 2MP photo and 720p HD camera, and four microphones. In regards to the input commands, HoloLens accepts four kinds of input: gaze, hand gesture, voice commands and any Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) input controllers (such as keyboard, mouse, gampad or clicker).
Go back to Hardware Resources